Sustainability


TESS Group Initiatives in Response
to TCFD Recommendations
The TESS Group expressed support for the recommendation of the Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD), which had been founded by the Financial Stability Board (FSB). TheTCFD recommendations request that information be disclosed about climate change-related governance,strategy, risk management, and indicators and targets. In line with the recommendations, the TESS Group disclosed relevant information.

Governance
- Board of Directors supervisory system
- The TESS Group, focusing on the business areas of “renewable energy as the main power source,” “energy efficiency maximization,” and “intelligent energy infrastructure,” does not limit its climate change response to a risk management perspective but recognizes it to be one of the material management issues in terms of creating business opportunities. Our Board of Directors supervises and instructs each of the departments and subsidiaries by formulating management strategies and the medium-term management plan as well as managing various initiatives and business targets, etc., from both risk management and business creation aspects while taking into account response to climate change. From the perspective of strengthening oversight of the Group’s sustainability initiatives, including climate change responses, the Board of Directors passed a resolution in June 2022 to establish an ESG Promotion Committee under its supervision, with the officer in charge of ESG as a chairperson, and the ESG Promotion Committee was established on July 1 of the same year.
- Role of the management
- In order to enhance the Group’s initiatives for sustainability, including response to climate change, TESS Holdings has appointed an officer in charge of ESG and established an ESG Promotion Committee chaired by the said officer. The ESG Promotion Committee identifies materiality issues by extracting and analyzing potential ESG-related risks and opportunities in the Group’s business activities, studies countermeasures, and manages the progress of such measures. In addition, a working group for climate change response has been set up as a subsidiary body of the ESG Promotion Committee that examines specific measures for initiatives on the identified materiality issues and other individual themes.
Strategy
- Climate change risks and opportunities and their impact on business, strategy, and financial planning of the organization
-
The TESS Group identified physical and transition risks and business opportunities associated with climate change and assessed the effects of those risks and opportunities in our business strategies and financial planning. A scenario analysis was conducted using 2-degree and 4-degree scenarios during risk identification. We studied transitional risks assumed to be materialized in 2-degree scenarios such as IEA’s SDS and physical risks similarly predicted in IPCC’s RCP8.5 and other 4-degree scenarios.
Under the 2-degree scenarios, the principal risks and opportunities for the TESS Group include 1) tighter regulations by the government and other bodies, 2) technological progress, 3) higher raw material costs caused by crude oil price hikes from delayed development of new oil fields, and 4) reputation among investors. Specifically, the main risks associated with 1) tighter regulations by the government and other bodies include higher energy costs (e.g., electricity, gas) and raw material costs due to the introduction of a carbon tax and GHG emission restrictions. Regarding 2) technological progress, to maintain a competitive advantage of its energy solution offerings, the TESS Group needs to actively invest in a broad range of decarbonizing technologies such as biomass, storage batteries, and hydrogen, which will incur risks such as results not being produced as initially planned. About 3) higher raw material costs caused by crude oil price hikes, there is the risk of natural gas price hikes for the Group’s co-generation systems. As for 4) our reputation among investors, the Group’s corporate brand, backed by the transition to a decarbonized society, will be damaged in case of failing to appropriately disclose climate-related risks and other factors, which will create risks including falling stock prices and increased fund procurement costs.
Meanwhile, under the 4-degree scenario, a study mainly of physical risks shows acute risks such as the effects of increasingly stronger typhoons and flooding due to torrential rain on power plants owned by the TESS Group (including impacts such as extended construction periods resulting from disruptions in the supply chain). Chronic risks include changes in weather patterns causing decreasing amounts of solar radiation, which in turn cause a lower quantity of power generated in our solar power plants, an elevation in average temperatures causing a rise in energy consumption levels, decreasing efficiency in workplaces, and decreasing power generation efficiency in our solar power plants. Among the acute risks of physical risks, the risk of wind and flood damages to our solar power plants (including lost profits) is covered by insurance and other means.
The opportunities include 1) further lowering of emissions in our use of energy sources, 2) development and expansion of low-carbon-emitting products and services, 3) development of new products and services through R&D and innovation, 4) access to new markets, and 5) promotion of resilience-response business. With regard to 1) lower emissions in the use of energy sources and 2) development and expansion of low-carbon-emitting products and services, we expect an increase in revenue from growing demand for renewable energy, such as on-site PPA (Power Purchase Agreement ; self-consumption solar power generation system) and biomass power generation due to heightening decarbonization needs. Regarding 3) R&D and innovation, we expect to increase revenue by developing and commercializing the optimization business with storage batteries for energy management systems. As for 4) new markets, we assume a growing customer base and revenue increase as a result of utilizing and transferring our energy conservation and renewable energy technologies, which have been developed since our inception for energy-intensive factories and work sites, to new sectors (e.g., SMEs, local governments) in a decarbonized society. An increase in revenue due to increasing demand for products and services associated with 5) securing resilience (e.g., installation of self-generating equipment [co-generation system] and on-site PPA as BCP) is also assumed.
- Resilience of organizational strategy that takes into consideration climate-related scenarios, including a scenario for below 2 degrees
- Risks identified with the 2-degree and 4-degree scenarios is shared with the officer in charge of ESG, the ESG Promotion Committee members and others, and by appropriately addressing the risks, the advantageous position ofthe Group’s business strengths (business opportunities) can be secured, while also ensuring resilience against climate-related risks. We will continue to address climate change by refining scenario analysis and financial impact assessment and by specifically reflecting measures for risks and opportunities in the management plan.
Summary of Scenario Analysis (Transition Risks, Physical Risks, Opportunities)
Transition Risks
Major
CategoryMedium
CategoryMinor
CategoryPotential Financial Impact Level of Impact
(Low/Medium/High)Transition risks
(2-degree scenario)Policy and legal risk Introduction of carbon pricing (e.g., carbon tax, etc.) ・Increase in costs of various raw materials such as energy due to the introduction of a carbon tax
Low Adoption of carbon emission targets and scheme for emission quota allocation within companies ・Risk of constraints on business activities as a result of CO₂ emission restrictions, etc.
・Increase in costs of emission allowances through emissions trading and green electricity purchase to achieve imposed emissions targets
・Increase in investments for energy efficiency
Low Increase in litigation risk ・Risk of reputation damage due to failure to meet emission targets or inadequate information disclosure, and increase in costs related to handling such situations
・Increase in costs for handling litigations related to the development of renewable energy power plants
High Technology risk Investment into new technologies ・Increase in capital investment and R&D costs for developing new technologies and services related to biomass, storage batteries, hydrogen, intercompany aggregation business, etc., and risk of related failures.
Medium Market risk Changes in customer behavior ・Increase in costs to meet customers’ needs for even lower carbon emission services and products (including electricity, heat, etc.)
・Increase in costs to comply with stricter low carbon/decarbonization requirements in the preconditions for bidding
・Decrease in demand for power generating facilities that use fossil fuels
Low Rise in raw material costs ・Increase in costs of raw materials, energy, and electricity
Medium Reputation risk Changes in expectations of customers and local communities ・Increase in operating costs for addressing climate-related issues and for information disclosure
・Losing customers as a result of inadequate response or disclosure causing degrading reputation
・Scaling down or exiting a business that is negatively affecting the environment
Low Changes in expectations of investors ・Falling stock prices or losing investors as a result of inadequately addressing climate-related issues or inadequate handling of information disclosure needs
Medium Physical Risks
Major
CategoryMedium
CategoryMinor
CategoryPotential Financial Impact Level of Impact
(Low/Medium/High)Physical risks
(4-degree scenario)Acute risk Greater magnitude and frequency of natural disasters caused by intensifying extreme weather ・Damage incurred upon employees, workplaces, company facilities and company-owned power plants by typhoons, tornados, and floods
・Increase in insurance premiums
・Increase in risk of extended construction periods due to suspended operations at disaster-hit workplaces/suppliers or delayed material deliveries caused by a break in the supply chain, and of violating contractual obligations
Medium Chronic risk Changes in precipitation patterns and extreme changes in weather patterns ・Decrease revenue from electricity sales from company-owned solar power plants due to increased precipitation and number of days of rainfall
Medium Elevation in average temperatures ・Increase in costs with increased energy usage
・Decrease in productivity resulting from an increase in health issues of on-site workers (heatstroke, etc.) and avoiding work during extreme heat hours
・Decrease revenue from electricity sales from company-owned solar power plants due to lower generating efficiency
Medium Opportunities
Medium
CategoryMinor
CategoryPotential Financial Impact Level of Impact
(Low/Medium/High)Resource efficiency Investment in measures for worksites ・Decrease in automobile fuel costs by replacing company cars with next-generation vehicles
Low Energy source Utilization of energy sources with even lower emissions ・Reduction in GHG emissions through procurement of renewable energy electricity, etc.
・Reduction in GHG emissions and fuel costs by promoting the use of energy conservation systems such as co-generation systems
・Decrease in exposure in case fossil fuel costs rise in the future
・Advantages in terms of reputation leading to an increase in demand for products and services
High Usage of new technologies ・Advantages in terms of reputation leading to an increase in demand for products and services
・Decreases in GHG emissions and fuel costs through improved energy efficiency
・Decrease in exposure in case fossil fuel costs rise in the future
Medium Products and services Development and spread of low carbon emission products and services ・Increase in revenue with greater demand for construction work related to renewable energy, such as solar power generation and biomass power generation, amidst heightened decarbonization needs
・Increase in revenue due to growing demand from renewal work toward improvement in the energy efficiency of existing facilities to meet stricter energy conservation regulations
・Revenue from investments in renewable energy power plants, including on-site PPA
High Development of new products and services with R&D and innovation ・Increase in revenue from development and adoption of biomass fuel
・Increase in revenue from development and adoption of hydrogen energy utilization systems
・Increase in revenue from development and implementation of business to make energy management systems more efficient using storage batteries
High Ability to diversify business operations ・Growth in the number of customers and increase in revenue as a result of transferring and utilizing technologies related to energy conservation and renewable energy, which have been developed since our inception for heavy energy-consuming factories and work sites, to new sectors (SMEs, local governments, etc.) in a decarbonized society
Medium Expectations from customers and investors ・Showing that the Group’s business itself is in supporting decarbonization and shift to low carbon leading to a good reputation among customers and investors, which will raise our corporate value
・The company’s proactive initiatives for ESG issues and disclosure of their progress, and a call for ESG investment will increase stock prices and further raise our corporate value
Medium Markets Access to new markets ・Growth in the number of customers and increase in revenue as a result of transferring and utilizing technologies related to energy conservation and renewable energy, which have been developed since our inception for heavy energy-consuming factories and work sites, to new sectors (SMEs, local governments, etc.) in a decarbonized society
・Increase in revenue and in opportunities for receiving orders from growing needs in adapting to climate change
High Use of public sector incentives ・Increase in revenue from growth in opportunities for receiving orders with incentives for subsidy programs and others to encourage capital investment for energy conservation and renewable energy
Medium Reputation ・Increase in corporate value through low carbon/decarbonization business expansion and obtaining various fund procurement opportunities
Medium Resilience Promotion of resilience response business ・Increase in revenue as a result of growing demand for products and services related to securing resilience (e.g., installation of self-generating equipment [co-generation system] and on-site PPA as BCP)
・Increase in revenue opportunities arising from expedited construction work and facility renewals for strengthening facilities
・Increase in revenue from capital investment to strengthen areas with a high risk of natural disasters such as flooding and an increasing number of construction work for relocation to safer places
High
Risk Management
- Process used by the organization to identify and assess climate-related risks
- The ESG Promotion Committee within the TESS Group identifies and assesses climate-related risks. Specifically, transition and physical risks associated with climate change are identified and assessed in light of scenario analysis.
- Process used by the organization to manage climate-related risks
- Material risks, including identified and assessed climate-related risks, have been reported and shared with the Board of Directors and others as appropriate in cooperation with the Compliance Risk Management Committee, and suitable countermeasures are being examined. Specifically, out of climate change-related risks, those posing a severe impact on the Group’s management will be deliberated as appropriate by the Board of Directors, and each department and subsidiary will be given instructions and reporting through which countermeasures will be examined to avoid the occurrence of risk events and determine the situation’s handling if it occurred.
- Overall integration of the organization for risk management
- With regard to the overall risk management structure at TESS Holdings, along with the establishment of the Compliance Risk Management Committee, the Risk Management Regulations have been formulated and their appropriate application is being carried out. Specifically, should a material event occur over the course of business activities, it is reported to the Compliance Risk Management Committee, and a structure is in place for deliberations to take place as necessary regarding the handling of the situation. Also, a system has been established whereby outside experts such as attorneys, auditors, and tax accountants are available for advice to detect risks early and prevent their occurrence. With regard to sustainability risks, including climate change risks identified and assessed by the ESG Promotion Committee as potentially having a significant impact on the TESS Group, countermeasures are reviewed in cooperation with the Compliance Risk Management Committee.
Indicators and Targets
- Metrics used in assessing climate-related risks and opportunities
-
The TESS Group applies GHG emissions (Scopes 1+2 in tons CO₂e) and our renewable energy power plant transmission of electricity (MWh) and resulting contribution to CO₂ emission reduction amount (in tons CO₂) as indicators in assessing risks and opportunities associated with climate change. GHG emissions for the TESS Group are as indicated in the chart below (TESS Group GHG Emissions Trend and Targets). In FYE June 2024, the Group reduced Scope 1+2 GHG emissions to virtually zero. This was made possible by strengthening energy-saving measures in offices (installing high-efficiency lighting fixtures and equipment) and using hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs) for company vehicles. The emissions remained after these efforts were offset by using J-Credits generated by our customers. Thereby, we were able to achieve the goal of reducing Scope 1+2 GHG emissions to zero in FYE June 2024. We are planning to set a separate GHG emissions target for FYE June 2025 and beyond, taking into account the impact of the biomass fuel production and retail business in Indonesia, which are scheduled to be fully operational in coming years. Regarding GHG emissions within Japan, we intend to maintain zero GHG emissions, and for FYE June 2025, the Group reduced Scope 1+2 GHG emissions to virtually zero through similar efforts as those detailed above. In addition, the data for Scope 3 GHG emissions has been compiled starting in FYE June 2023. For FYE June 2023, data for TESS Holdings and our core subsidiary, TESS Engineering Co., Ltd. was aggregated, resulting in approximately 557,000 tons CO₂e. The emissions for FYE June 2024 and beyond were calculated by including emissions of other consolidated subsidiaries, resulting in approximately 323,000 tons CO₂e for FYE June 2024 and approximately 476,000 tons CO₂e for FYE June 2025. Our renewable energy power plant transmission of electricity (MWh) and resulting contribution to CO₂ emission reduction amount (in tons CO₂ ) are as indicated in the chart below (TESS Group Transmission of Electricity and Contribution to CO₂ Emission Reduction Amount Trend and Targets). We are aiming to achieve 749,000MWh for our renewable energy power plant transmission of electricity and 321,000 tons CO₂ for the resulting contribution to CO₂ emission reduction by FYE June 2030.
-
- Chart:TESS Group GHG Emissions Trend and Targets
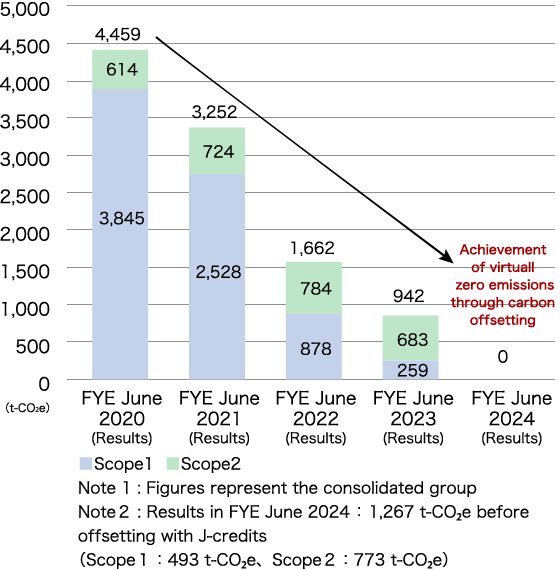
-
- Chart: TESS Group Transmission of Electricity and Contribution
to CO₂ Emission Reduction Amount Trend and Targets 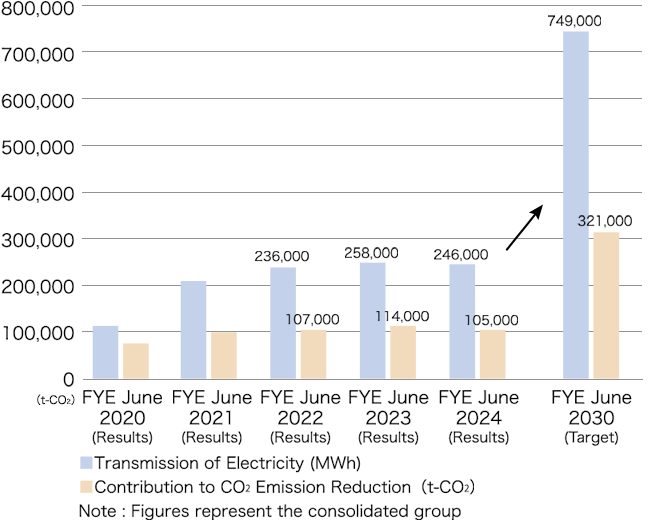
- Chart: TESS Group Transmission of Electricity and Contribution
-
